题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| assume cs:codesg
codesg segment
mov ax,4c00h
int 21h
start:
mov ax,0
s:
nop
nop
mov di,offect s
mov si,offect s2
mov ax,cs:[si]
mov cs:[di],ax
s0:
jump short s
s1:
mov ax,0
int 21h
mov ax,0
s2:
jmp short s1
nop
codesg ends
end start
|
这段代码首先用
mov di,offect s
mov si,offect s2
mov ax,cs:[si]
mov cs:[di],ax
将s2处代码写到s处
然后接着执行s0,跳到s,执行被写入的jmp short s1
关键来了
汇编中jmp short X的本质是由编译器计算出当前地址举例要跳转标号的偏移值
再进行相对偏移;
所以jmp short s1实际是向前跳8个字节的意思(mov ax,0 int 21h mov ax,0这三条指令长8个字节)到原来的s1
但现在这句话被简单拷贝在了s处,电脑则也只是向前跳8个字节(不管前面到哪里),所以ip指针会向前执行到mov ax,4c00h处(mov ax,4c00h int 21h mov ax,0也是8个字节长)最后结束
另一个实用的程序
属性字节格式:
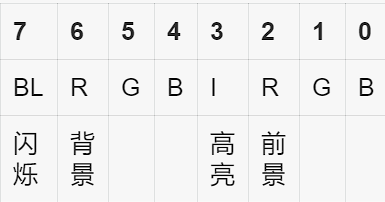
(二进制)
16*16=256=2^8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| assume cs:code,ds:data
data segment
dw 1920,2080,2240,64
db 'welcome to dyinj'
db 82h,0ach,0f9h
data ends
code segment
start:
mov ax,data
mov ds,ax
mov ax,0B800h
mov es,ax
mov cx,3
xor di,di
xor si,si
s1:
mov ax,di
mov bl,2
div bl
mov si,ax
mov ah,[si+24]
mov si,ds:[6]
mov bp,[di]
mov dx,cx
mov bx,0
mov cx,16
s2:
mov al,[bx+8]
mov es:[bp+si],al
mov es:[bp+si+1],ah
inc bx
add si,2
loop s2
mov cx,dx
add di,2
loop s1
mov ax,4c00h
int 21h
code ends
end start
|
ret/retf
和上一章不同在于用的是栈
pop栈中数据给指令指针
回忆:PUSH在存放数据时 SP先减二再取数据;POP 先拿数据再SP加二
ret
指令用栈中的数据,修改IP的内容,从而实现近转移
- (IP) = ((ss)*16 + (sp))
- (SP) = (sp) + 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| assume cs:code
stack segment
db 16 dup(0)
stack ends
code segment
mov ax, 4c00h
int 21h
start:
mov ax, stack
mov ss, ax
mov sp, 16
mov ax, 0
push ax
mov bx, 0
ret
code ends
end start
|
retf
指令用栈中的数据,修改CS和IP的内容,从而实现远转移
- (IP) = ((ss) * 16 + (sp))
- (SP) = (sp) + 2
- (CS) = ((ss) * 16 + (sp))
- (SP) = (sp) + 2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| assume cs:code
stack segment
db 16 dup(0)
stack ends
code segment
mov ax, 4c00h
int 21h
start:
mov ax, stack
mov ss, ax
mov sp, 16
mov ax, 0
push cs
push ax
mov bx, 0
retf
code ends
end start
|
call
call
- 将当前的ip或cs和ip压入栈中
- 转移
比jmp多了压栈
call s(标号)
(sp)=(sp)-2
((ss)*16+(sp))=ip
(ip)=(ip)+16位位移
16位位移=标号处地址-call指令后第一个字节的地址
范围-32768~332767
call far ptr s(标号)
(sp)=(sp)-2
((ss)*16+(sp))=(cs)
(sp)=(sp)-2
((ss)*16+(sp))=(ip)
(cs)=标号所在段地址
(ip)=标号所在段中的偏移地址
先压的是cs后压ip
call reg(16位寄存器)
(sp)=(sp)-2
((ss)*16+(sp))=(ip)
(ip)=(16位寄存器)
call word ptr s(标号)/call dword ptr s(标号)
函数
call和ret组合使用
求2的3次方存入bx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| assume cs:code
code segment
start:
mov ax,1
mov cx,3
call s
mov bx,ax
mov ax, 4c00h
int 21h
s:
add ax,ax
loop s
ret
code ends
end start
|
模块化
n的三次方
1
2
3
4
5
| cube:
mov ax,bx
mul bx
mul bx
ret
|
实例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| assume cs:code
data segment
dw 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
dd 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0
data ends
code segment
start:
mov ax,data
mov ds,ax
mov si,0
mov di,16
mov cx,8
s:
mov bx,[si]
call cube
mov [di],ax
mov [di+2],dx
add si,2
add di,4
loop s
mov ax,4c00h
int 21h
cube:
mov ax,bx
mul bx
mul bx
ret
code ends
end start
|
mul
- 两个相乘的数:要么都是8位,要么都是16位。如果是8位,一个默认放在al中,另一个放在8位reg或内存字节单元中;如果是16位,一个在AX中,另一个在16位reg或内存字单元中。
- 结果,如果是8位乘法,结果默认放在ax中;如果是16位乘法,结果高位默认在dx中存放,低位在ax中存放。
格式:mul reg或mul 内存单元
1
2
3
| mov al, 5h
mov bl, 10h
mul bl
|
