其实就是学别人代码
接口简述
比如:People是一个接口,他里面有say这个方法。
接口的定义:
1 | public interface People{ |
但是接口没有方法体。只能通过一个具体的类去实现其中的方法体。
比如 Chinese这个类,就实现了People这个接口。
接口的实现:
1 | public class Chinese implements People{ |
接口的调用:
1 | People chinese = new Chinese() ; |
关于Awt
关于 MouseListener接口
void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)在组件上单击(按下并释放)鼠标按钮时调用。void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e)鼠标进入组件时调用 。void mouseExited(MouseEvent e)鼠标退出组件时调用。void mousePressed(MouseEvent e)在组件上按下鼠标按钮时调用。void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e)在组件上释放鼠标按钮时调用。
实验与结合:
1 | package test; |
混合使用: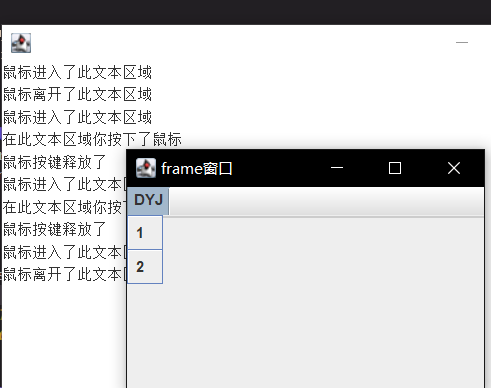
6. getX(),getY():获取鼠标的坐标位置
7. getModifiers():获取鼠标的左或右键
8. getClickCount():获取鼠标被点击的次数
9. setCursor():控制鼠标指针的形状。如设置成漏斗:setCursor(Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.WAIT_CURSOR))
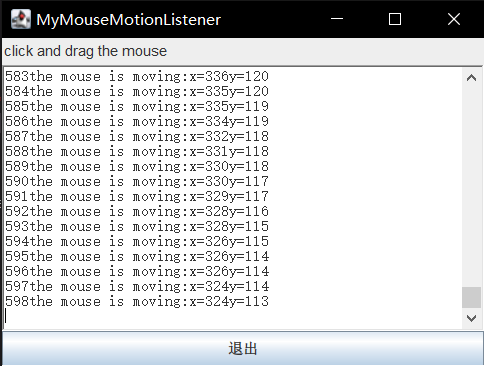
关于 MouseMotionListener接口
void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e)在组件上按下鼠标按钮然后拖动时调用。void mouseMoved(MouseEvent e)将鼠标光标移动到组件但未按下任何按钮时调用。
简单例子:效果:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60package test;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JButton;
public class test2 implements MouseMotionListener {
JFrame myframe; // JFrame通常默认使用BorderLayout布局管理器的
TextArea tf;
JButton exitButton;
int number = 1;
public test2() {
Label label = new Label("click and drag the mouse");
myframe = new JFrame("MyMouseMotionListener");
tf = new TextArea();
exitButton = new JButton("退出");
tf.addMouseMotionListener(this);
exitButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
myframe.add(label, BorderLayout.NORTH);
myframe.add(tf, BorderLayout.CENTER);
myframe.add(exitButton, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
myframe.setSize(400, 300);
myframe.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new test2();
}
// 负责处理鼠标拖动事件
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) {
//getX(),getY():获取鼠标的坐标位置
String s = number++ + "" + "the mouse is draggered:x=" + e.getX()
+ "y=" + e.getY() + "\n";
tf.append(s);
}
// 负责处理鼠标移动事件
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent e) {
String s = number++ + "" + "the mouse is moving:x=" + e.getX() + "y="
+ e.getY() + "\n";
tf.append(s);
}
}
关于Swing
跨平台性的更丰富的图形界面
首先关于JFrame
窗体容器,Swing组件的载体。继承自Frame类。
并且可直接使用jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);关闭窗体
关于JDialog
对话框,继承自Dialog类,功能是从一个窗体钟弹出另一个窗体(类似子JFrame)
使用public JDialog(Frame f, String title, boolean model)创建一个指定窗体、标题和模式的对话框。
关于JLabel
JLabel类可以显示文本或图像。通过在显示区域中设置垂直和水平对齐来对齐标签的内容。默认情况下,标签在显示区域中垂直居中。默认情况下,纯文本标签前沿对齐; 默认情况下,仅图像标签水平居中。
例:
1 | JLabel(Icon image, int horizontalAlignment);//使用指定的图像和水平对齐创建JLabel实例。 |
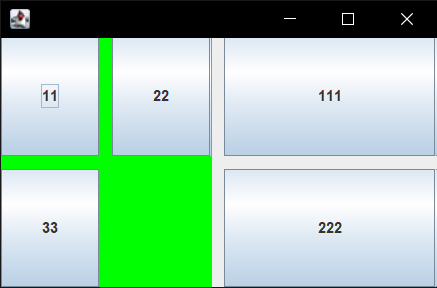
中间容器JPanel
中间性区域安排
1 | package test; |
关于JScrollPane
JScrollPane内只能添加一个组件,是一个带滚动条的面板
1 | package test; |
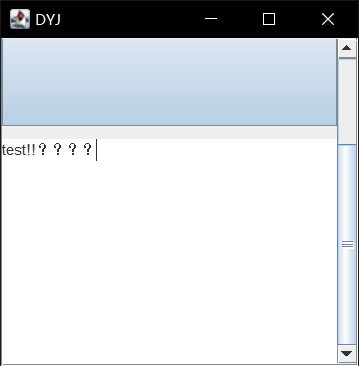
它在界面需要时才自动出现
关于JMenuBar
JMenuBar,菜单栏。菜单栏组件添加到 JFrame 窗口后,在窗口的内容显示区域的顶部出现。实现一个菜单栏主要涉及三种类:
- JMenuBar 表示一个菜单栏。
- JMenu 表示菜单栏上的一个一级菜单。
- JMenuItem, JCheckBoxMenuItem, JRadioButtonMenuItem 表示一级菜单下的一个子菜单项,三者分别表示 普通的子菜单、带复选框的子菜单、带单选按钮的子菜单。
使用:效果:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
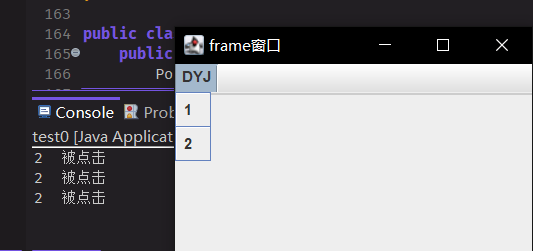
29class Batton{
void view() {
JFrame f = new JFrame("frame窗口");
f.setSize(300,200);
f.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//叉号能关
JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();//创建菜单栏
JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("DYJ");
menuBar.add(fileMenu);//一级菜单的创建与添加
JMenuItem testMenuItem = new JMenuItem("1");
JMenuItem exitMenuItem = new JMenuItem("2");//子选项
fileMenu.add(testMenuItem);//子选项添加
fileMenu.addSeparator();//添加分割线
fileMenu.add(exitMenuItem);
exitMenuItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("2 被点击");
}
});
f.setJMenuBar(menuBar);//设置到窗口
f.setVisible(true);//设置开启显示
}
}
默认功能:1
jRMItemEasy.setSelected(true);// 默认按钮选择